- Content
- Overview
- Introduction
- JS where to
Where to insert JavaScript code?
In HTML, JavaScript code is inserted between <script> and </script> tags.
JavaScript Example 1
<!DOCTYPE><html> <body> <h1> JavaScript Example</h1> <script> document.write("Hey there! This is JavaScript tutorial");</script> </body> </html> Output

The script tag specifies that we are using JavaScript.
Note: Old JavaScript examples may use a type attribute: <script type="text/javascript">.
The type attribute is not required. JavaScript is the default scripting language in HTML.
JavaScript in <head>
In this example we use a function, a JavaScript function is added in the <head> section of an HTML page.
Note: A JavaScript function is a section of JavaScript code that can be executed when "called." A function, for example, can be invoked when an event occurs, such as when a user clicks a button. However, You will learn much more about functions in later chapters.
The function myFunction is called when a button is clicked:
<!DOCTYPE><html> <body> <head><script>function myFunction() { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Paragraph changed."; }
</script></head><h1> This is my heading</h1> <p> This is my heading</p> <p id="demo">A paragraph we have.
</p><button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Click me! </button> </body> </html> Output 1: Before click
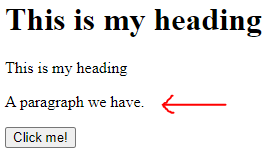
Output 2: After click
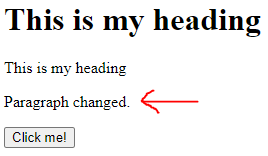
JavaScript in <body>
In this example, a JavaScript function is placed in the <body> section of an HTML page.
The function is called when a button is clicked:
<html> <body> <h1> This is my heading</h1> <script>function myFunction() { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "The button clicked then, the paragraph changed."; }
</script><p id="demo">This is the paragraph.
</p><button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Click me! </button> </body> </html> Output 1: Before click

Output 2: After click
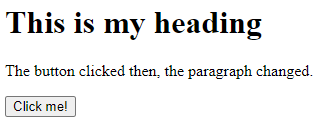
Here are some things to keep in mind:
Note: Because script interpretation slows down the display, placing scripts at the bottom of the </body> element increases display speed.
External JavaScript
Additionally, scripts may be stored in external files:
External file: myScript.js
You can place an external script reference in <head> or <body> as you like.
The script will behave as if it is located exactly where the <script> tag is located.
Note: External scripts cannot contain <script> tag.
HTML file: index.html
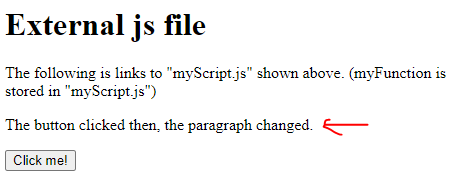
<html> <body> <h1> External js file</h1> The following is links to "myScript.js" shown above.
(myFunction is stored in "myScript.js")
<script src="myScript.js"></script><p id="demo">This is the first paragraph.
</p><button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Click me! </button> </body> </html> Output 1: Before click
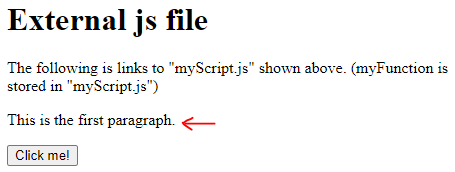
Output 2: After click
.
Advantages Of External JavaScript
- It keeps HTML and code separate.
- It simplifies the reading and maintenance of HTML and JavaScript.
- JavaScript files that have been cached can help to speed up page loads.
External References
There are three possible ways to reference an external script:
- With a file path (like /js/)
- With a full URL (a full web address)
- Without any path
<script src="/js/myScript.js"></script>
<script src="https://www.softechsupply.com/js/myScript.js"></script>
<script src="myScript.js"></script>




