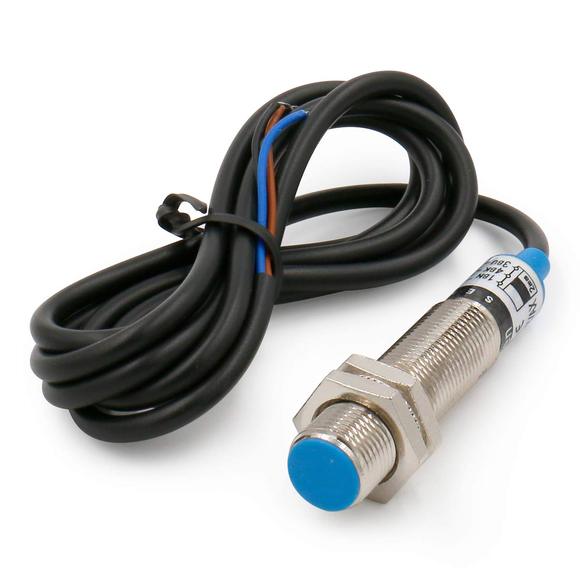
Capacitive Proximity Sensor
Price:
RWF 15,000Added to Cart!
Need help or have questions about this product?
Contact STS Support →Product Description
- Outward appearance code:12mm
- Outward appearance code: Wetal shell
- Detection distance: 4mm
- Working voltage: DC 5-36V
- Polarity: NPN
- Dimention: 12 x 50mm
Capacitive Proximity Sensors Working Principle
Capacitive proximity sensors rely on the ability of objects to hold an electrical charge even when the object is non-conductive. Capacitance is a measure of the amount of charge that can be stored under the application of an applied voltage. The sensor operates by noting the change in capacitance that occurs when an object (usually called the �target�) approaches the sensor.
Major Features of Capacitive Sensors
For both capacitive and inductive proximity sensors, hysteresis is an important operating characteristic. Hysteresis is determined by the difference between the sensing face and target detection distance, and the sensing face and target release distance. These traits dictate the delineating line between object detection and non-detection. But despite their similarities to inductive sensors, capacitive sensors have a number of distinct features, including:
The ability to detect nonmetallic objects.
The ability to detect small lightweight objects that cannot be picked up by mechanical limit switches.
A solid-state output that does not bounce its contact signal.
A high switching rate that provides quick reaction in object counting applications.
The ability to detect liquid targets through certain barriers.
A long operational lifespan.
Although capacitive proximity sensors are useful for a range of applications, they can be negatively influenced by elevated levels of humidity and moisture. In addition, their sensing field must be relatively broad in order to provide effective detection.
Capacitive Sensing Range
Capacitive Proximity Sensor usually have a larger sensing distance than their inductive counterparts, and it typically falls between 4 and 40 millimeters. The detection range depends on plate diameter, as capacitive sensors measure dielectric gaps. Many capacitive proximity sensors are equipped with sensitivity adjustment controls for the sensing distance, allowing them to compensate for target object and application conditions.
Why Buy from SoftTech Supply?
- Genuine electronic components from trusted suppliers
- Competitive prices on Arduino, Raspberry Pi, sensors & more
- Fast delivery across Kigali and Rwanda
- Expert technical support and project consultation
- Easy returns and quality guarantee
Related Products
Buy Capacitive Proximity Sensor at STS - Kigali, Rwanda
Capacitive Proximity Sensor is available at SoftTech Supply, your trusted electronics shop in Kigali, Rwanda. We stock genuine electronic components including Arduino boards, Raspberry Pi, ESP32, ESP8266, various sensors, motors, displays, and thousands of other components for your IoT, embedded systems, and electronics projects. Visit our shop or order online for fast delivery across Rwanda. Need help selecting components or implementing your project? Contact STS for expert technical support and consultation.